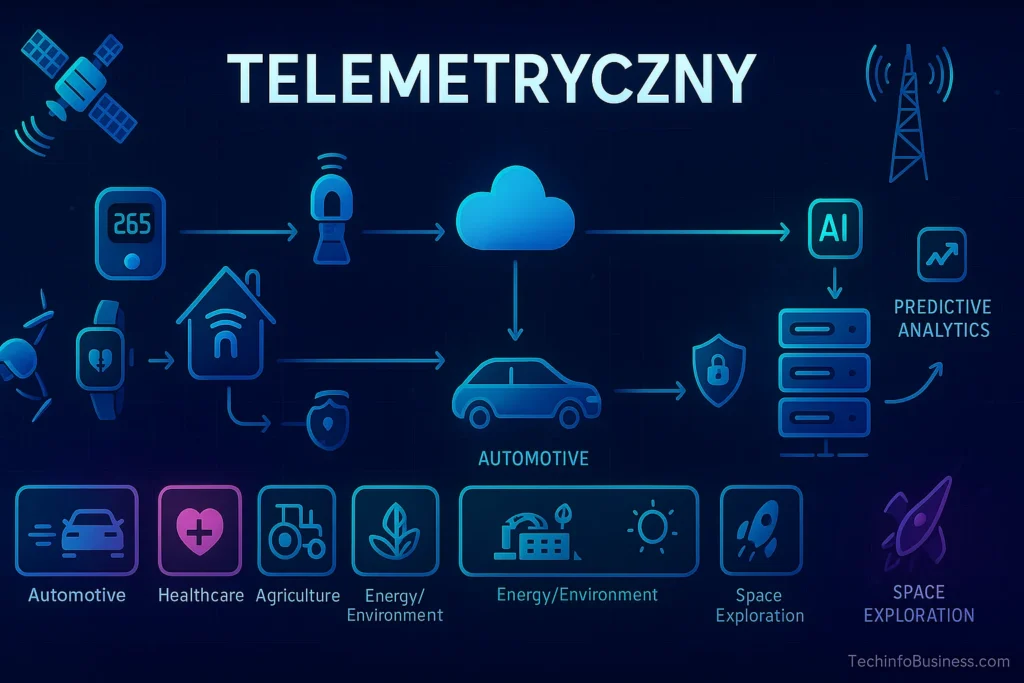
Introduction to Telemetryczny
The concept of telemetryczny revolves around the use of technology to gather, transmit, and analyse information across different sectors. In today’s data-driven world, businesses and industries rely heavily on real-time data, real-time information, and real-time insights to make faster and more accurate decisions. By using advanced communication networks and a reliable transmission channel, telemetry systems enable remote monitoring of assets, equipment, and environments.
Core Technologies and Infrastructure
Modern telemetry depends on a variety of core technologies. Data transmission often relies on GSM/GPRS modules, karta SIM, cellular connections, satellite links, and satellite signals. Many setups include moduły RTU for local data collection, and sometimes transmisja spontaniczna for quick updates without manual prompting. A central system processes the incoming information and integrates it with a cloud platform, cloud infrastructure, or cloud computing environment. This infrastructure is enhanced further by edge computing, powerful processing units, and an analytics engine that makes sense of the raw data.
To ensure accuracy, industries often use systemy telemetryczne, systemy telemetryczne i teleinformatyczne, and even system narzędzi combined with systemy SCADA for advanced control. In addition, systemy bateryjne and data logger devices support long-term operations, while a receiver station collects information from multiple channels.
Telemetry in IoT and Smart Environments
The Internet of Things is closely tied to telemetry. Devices such as smart meters, wearable devices, sensor belts, and wearable health devices provide valuable data. In smart homes and smart cities, telemetry supports real-time tracking and helps improve sustainability. With the rollout of 5G and 6G connectivity, telemetry now integrates with V2X communication, ensuring autonomous vehicles and self-driving cars can exchange data securely.
The growth of przemysłowy internet rzeczy (industrial IoT) combined with technologie mobilne makes it possible to connect millions of devices simultaneously. Specialised gateways such as the brama komunikacyjna MT-221 play a critical role in linking devices across multiple systems.
Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics
Telemetry data becomes more powerful when combined with artificial intelligence and Machine Learning. Through machine learning models and AI-powered algorithms, organisations can achieve predictive analytics and predictive maintenance. These insights are particularly useful in manufacturing plants, the automotive industry, and other fields where efficiency matters.
By examining performance metrics, machine performance metrics, and data monitoring, businesses can optimise processes. Tools such as big data analytics, cloud-based analytics, and even quantum communication expand the possibilities further.
Industry Applications of Telemetryczny
Telemetry applications can be found across multiple sectors:
- Automotive technologies: From vehicle telemetry systems to GPS trackers, OBD-II modules, and GPS-based fleet management systems, cars and trucks are now deeply connected. This improves fleet management efficiency and safety.
- Agriculture: Farmers benefit from precision farming methods, which use telemetry to monitor soil moisture levels, crop conditions, and weather patterns.
- Energy and Environment: Utilities rely on system monitorowania środowiska to address climate change and ensure accurate temperature readings. Environmental monitoring helps prevent risks and ensures sustainability.
- Healthcare systems: The medical field uses telemetry for medical applications such as implanty ślimakowe, systemy telemetryczne w audiologii, and systemy telemedyczne. Hospitals also integrate wearable health devices for continuous patient observation.
- Space exploration: Space agencies rely on telemetry to track spacecraft and satellites, ensuring stable communication technologies and safe disaster warning systems.
- Industrial monitoring: Factories and production sites use telemetry for industrial monitoring, improving operations and connecting with system zarządzania danymi.
Security, Privacy, and Reliability
As telemetry systems expand, security and privacy become major concerns. Issues like data security, cybersecurity risks, and privacy breaches require advanced solutions. In regulated industries, a certyfikowany System Zarządzania Jakością ensures high standards, while systemy telemetryczne i teleinformatyczne maintain compliance and trust.
Benefits of Telemetryczny
There are several benefits of using telemetry systems:
- Remote measurement and monitoring save costs.
- Healthcare systems can track patients with wearable health devices.
- Predictive maintenance reduces downtime in manufacturing plants.
- Space exploration and automotive technologies gain precision and reliability.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many advantages, telemetry faces some hurdles. Managing huge volumes of data technologies is complex, especially when integrating with legacy setups. Connectivity issues in remote areas limit communication technologies, while ensuring data security in cloud computing remains a challenge. Moreover, standardisation across different moduły telemetryczne and protocols is still evolving.
Future of Telemetry Systems
The future of telemetryczny looks promising. With AI-powered algorithms, cloud-based analytics, and communication technologies, the field is set for rapid growth. Developments in autonomous vehicles, smart homes, and smart cities will benefit from faster networks like 5G and 6G connectivity. In healthcare, more advanced systemy telemedyczne will support patients at home, while in space, stronger satellite signals and quantum communication will transform space exploration.
Read More: Understanding IP2 Network and Its Impact on Modern Communication
Conclusion
Telemetry has become an essential part of the modern data-driven world. By combining sensing technologies, analytics engines, and secure communication technologies, industries can harness the power of real-time data. From precision farming and fleet management to space agencies and medical applications, telemetry systems continue to shape the future.
Even in cultural areas, the concept appears unexpectedly, as seen in terms like telenowela dokumentalna, showing how wide-ranging this field’s impact has become. Ultimately, telemetryczny represents more than just technology — it’s a foundation for innovation, safety, and smarter living across all industries.